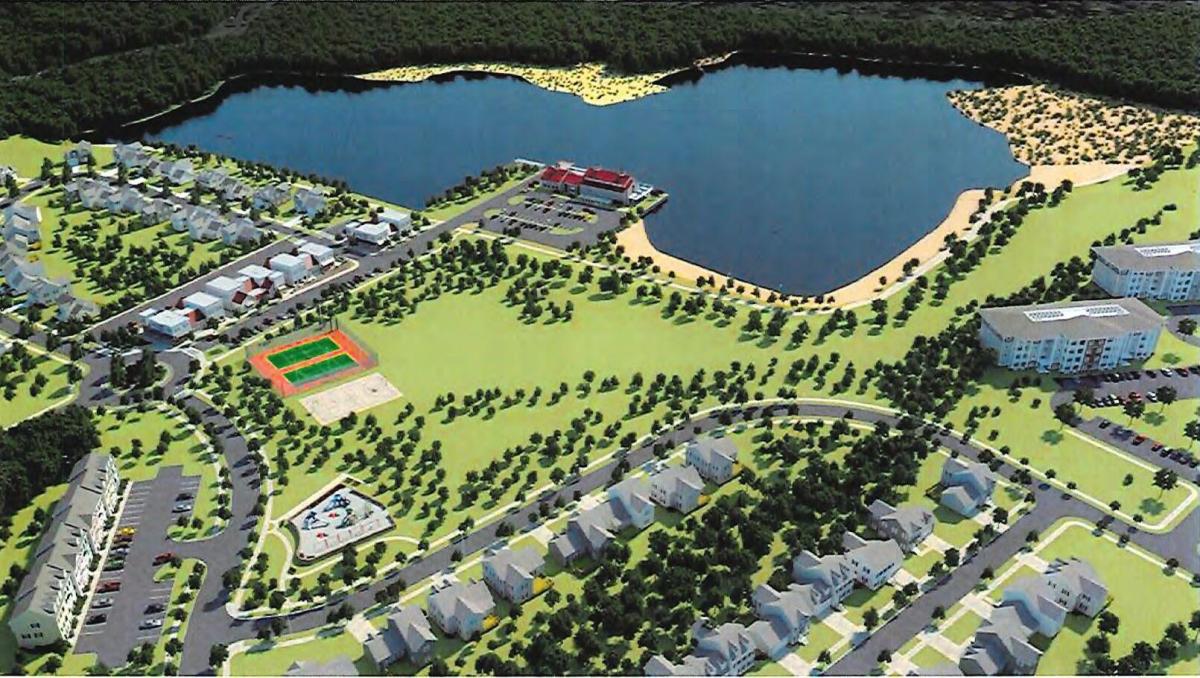
The county planning commission heard public comments Wednesday morning on Resolution 281 and will discuss Thursday night what actions, if any, it will take on the matter.
Resolution 281 amended Talbot County’s water and sewer plan to:
• reclassify and remap certain areas of the Lakeside/Trappe East property from W-2 to W-1 and from S-2 to S-1. (W-1 is immediate priority status for water; S-1 is immediate priority status for sewer.)
• add the Trappe East water and sewer systems to the list of capital improvement projects.
The commission’s agenda for Wednesday described the issue as “Discussion of Planning Commission’s previous certification of consistency with the Talbot County Comprehensive Plan with respect to Resolution 281 and possible recommendations and/or other actions, including undo, consider, reconsider, rescind or amend the previous certification.”
After hearing Wednesday morning from environmental groups and attorneys for a neighboring property owner, the developer, and the Town of Trappe, among others, Talbot County Planning Commission Chairman Phil “Chip” Councell asked for another meeting to be scheduled for the planning commission to consider the comments and discuss its course of action.
Councell asked for that meeting to be held before Tuesday, when the county council will hold a public hearing on Resolution 308, which would rescind adoption of Resolution 281. Resolution 308 was introduced by Council Vice President Pete Lesher, the sole council member to vote last year against Resolution 281.
Resolution 281 had been introduced Dec. 17, 2019, by Talbot County Councilmen Chuck Callahan, Frank Divilio, and Corey Pack, with public hearings held Feb. 11, 2020, and July 21, 2020.
The Talbot County Planning Commission considered the resolution in January, May, and June 2020, and voted 3-2 that an amended resolution was consistent with the comprehensive plan.
The county council voted 4-1 on Aug. 11, 2020, to approve the resolution as amended, sending the matter to the Maryland Department of the Environment for its approval, which the state agency subsequently granted. Councilwoman Laura Price joined Callahan, Divilio, and Pack in voting in favor of Resolution 281.
Earlier this year, petitioners asked the county council to rescind Resolution 281, claiming the county council and the planning commission were not provided with full information last year and noting that the discharge permit for the wastewater treatment plant that will serve Lakeside has been sent back to the state environment department for additional public comment and a public hearing.